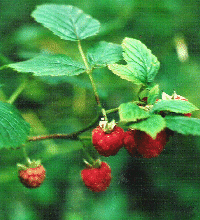
Raspberry

Sea Grape

Bilberry
Dispersal of Seeds by Animals
Animals of all sorts and sizes help plants to disperse their seeds. The method they use depends on the type of seed.
Seeds with attractive fruit or seeds
To attract the animals and birds and encourage them to act as seed carriers,
plants often surround their seeds with a brightly-coloured and sweet-tasting pulp.
 Raspberry |
 Sea Grape |
 Bilberry |
In the deserts of North Africa, elephants eat the fruits that have fallen from the trees and deposit the seeds in their droppings several miles away. In South American jungles, monkeys eat figs and other fruit, carrying some away in their stomachs and dropping others onto the ground. In Britain, foxes eat raspberries, squirrels eat nuts, blackbirds eat our strawberries, mice eat grass seeds, and in South Africa, even ants carry seeds into their nests, eat the tasty outer covering and leave the seeds to grow safely underground.
As well as eating them, some animals collect the fruits or seeds and bury them to eat later, but forget about them and the seeds germinate in their new location. Sometimes, as in the case of Mistletoe, the seeds are covered in a sticky slime which the birds rub off on a new tree. Even humans carry seeds far away for plants - by taking an apple on a picnic, for example, and throwing the core, with its seeds, into the bushes.
Examples of seeds spread by this method include:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
When animals take fruits or seeds for food, they act as willing transporters of the plant's seeds.
Sometimes, the plants make use of animals to carry their seeds without giving them any reward.
 Entelia |
 Lesser Burdock |
 Sea Holly |
Many plants produce fruits or individual seeds covered in hooks or spines which attach the seed to the animals's fur or feathers - or, in the case of humans, to our clothes or bags. The seeds are then carried a sufficient distance from the parent plant to give them space to grow. Eventually, the seed may fall off, or be rubbed off by the animal.
The most well-known plant of this type that we have in the UK is probably Goose Grass or Sticky Weed, which children throw at one another in a game, but in other countries there are larger such hitch-hikers which can damage animals when they become lodged between the animal's toes and cause infection and lameness. There's more information about species in North and South America that produce large hooked or prickly seedpods here.
Examples of seeds spread by this method include:
 |
 |
 |
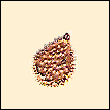 |
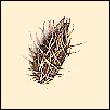 |
 |
| Back to the Seed Dispersal Main Page |
|---|