Fruits are the containers in which the plant puts its seeds. They are not all fruits as we think of them, but have many different forms. Some are fleshy with parts we like to eat, some are dry, some are heavy and are designed to be dispersed by falling and rolling away from the parent plant, some have wings or fluffy tails to enable them to be caught by the wind to be dispersed.
Fruits are divided into Fleshy Fruits, and Dry Fruits.
Fleshy Fruits can be subdivided again into those formed from a single flower and those formed from a group of flowers. They can have one seed or several seeds in.
Fleshy Fruits formed from a single flower are classified as: Berry, Drupe, Aggregation of Drupes, Pome, Hesperidium. Some authorities also give these separate status: Hep, Pseudocarp, Pepo.
Fleshy Fruits which grow from a group of flowers are: Sorosis, Synconium, Coenocarpium.
Dry Fruits can be divided into those in which the seeds are contained in a seedpod of some sort which opens to release the seeds (called Dehiscent), and those in which there isn't a seedpod which opens (Indehiscent).
Dry Dehiscent Fruits are Follicle, Legume, Silique, Capsule. Some authorities separate these further.
Dry Indehiscent Fruits are: Achene, Nut, Samara, Caryopsis. Some people sub-divide some of these further. There are also Schizocarpic Fruits.
Knowing the type of fruit a plant has might help you to identify it, and might also help you to know when the seeds are ready to harvest.
| FLESHY FRUITS formed from a single flower |
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Berry A Berry is a single fleshy fruit without a stone, usually containing a number of seeds. This is a Kiwi Fruit (Actinidia chinensis). Other fruits of this type are: Banana (Musa), Coffee (Coffea arabica), Currant (Ribes), Pasionfruit (Passiflora), Pepper (Capsicum), Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentus). |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Drupe A Drupe is a single fleshy fruit with a hard stone which contains the single seed. This is a Cherry (Prunus avium). Other fruits of this type are: Apricot (Prunus armeniaca), Plum (Prunus x domestica), Coconut (Cocos nucifera), Olive (Olea europaea), Peach (Prunus persica), Sloe (Prunus spinosa). |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Aggregation of Drupes An Aggregation of Drupes is a fleshy fruit, made up of many drupes but formed from a single flower, each drupe containing one seed. This is a Raspberry (Rubus idaeus). Other fruits of this type are: Loganberry (Rubus), Blackberry (Rubus fruticosus). |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Pome A Pome is a fleshy fruit with a thin skin, not formed from the ovary but from another part of the plant. These are sometimes called Accessory Fruits. The seeds are contained in chambers in the centre of the fruit. This is an Apple (Malus domestica). Other fruits of this type are: Firethorn (Pyracantha), Hawthorn (Crataegus), Medlar (Mespilus germanica), Pear (Pyrus communis), Quince (Cydonia oblonga). |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Hesperidium A Hesperidium is a berry with a tough, aromatic rind. This is an Orange (Citrus sinensis). Other fruits of this type are all Citrus fruits: Citron (Citrus medica), Grapefruit (Citrus x paradisi), Kumquat (Fortunella), Lemon (Citrus limon), Lime (Citrus aurantifolia). |
||||||||||||||||
There are other types of fleshy fruit which some people classify separately. A Hep or Hip is a fleshy fruit containing achenes, as in the Rose (Rosa); a Pepo is a fleshy fruit with a leathery skin, formed from an inferior ovary. This type of fruit is found only in members of the Gourd Family (Cucurbitaceae) - Cucumbers (Cucumis melo), Water Melon (Citrullus lanatus), Pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima), and Pseudocarp. |
|||||||||||||||||
 |
Pseudocarp A Pseudocarp is a false fruit, because it does not contain the seeds. The seeds are achenes, on the outside of a fleshy fruit. This is a Strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa). |
||||||||||||||||
| FLESHY FRUITS formed from a group of flowers |
|||||||||||||||||
| There are a few fruits formed from a group of flowers (inflorescence) rather than just one, but which form only one fruit. These are Sorosis, as in the Mulberry (Morus), Syngonium, as in the Fig (Ficus), and Coenocarpium, as in the Pineapple (Ananas). | DRY DEHISCENT FRUITS |
||||||||||||||||
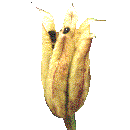 |
Follicle A Follicle is a dry dehiscent fruit which splits on one side only. It may contain one or many seeds. This is the fruit of a Columbine (Aquilegia). Other fruits of this type are: Delphinium (Delphinium), Larkspur (Consolida), Love in a Mist (Nigella damascena), Milkweed (Asclepias), Peony (Paeonia). |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Legume A Legume is a dry dehiscent pod that splits on two sides. This is the fruit of a Sweet Pea (Lathyrus odoratus). Other fruits of this type are all in members of the Pea Family (Leguminosae/Fabaceae): Acacia (Acacia), Alfalfa (Medicago sativa), Liquorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra), Flamboyant (Delonix regia), Pea (Pisum sativa), Peanut (Arachis hypogaea), Redbud (Cercis occidentalis), Runner Bean (Phaseolus coccineus), Wisteria (Wisteria). |
||||||||||||||||
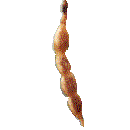 |
Lomentum A Lomentum is a dry dehiscent fruit, a legume constricted between the seeds. This is the fruit of a Golden Chain Tree (Laburnum anagyroides). Other fruits of this type are: Sophora (Sophora), Tick Trefoil (Desmodium). |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Silique A Silique is a dry dehiscent fruit. It is long and thin, splits down the two long sides, and has a papery membrane (the septum) between the two halves. This is the fruit of a Wallflower (Erysimum cheiri). Other fruits of this type are all in members of the Cabbage Family (Brassicaceae): Aubrieta (Aubrieta x cultorum), Cabbage (Brassica olearacea), Honesty (Lunaria annua), Radish (Raphanus sativus). A silique which is less than twice as long as broad is called a Silicula. |
||||||||||||||||
| . | Capsule A Capsule is the most common fruit type. A Capsule is a dry fruit which splits open to release the seeds. These plants all have fruit capsules: Cotton (Gossypium), Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus), Horse Chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum), Jimson Weed (Datura), Mahogany (Afzelia), Witch Hazel (Hamamelis). There are several types of Capsule, depending on how the fruit splits. |
||||||||||||||||
 |
Valvate Capsule A Valvate Capsule is a dry dehiscent fruit in which the tips of the seed capsule split. This is the fruit of a Campion (Silene). Other fruits of this type are: Jacob's Ladder (Polemonium), Pink (Dianthus), Primrose (Primula). | ||||||||||||||||
 |
Porose Capsule A Porose Capsule is a dry dehiscent fruit, opening with pores or holes around the top. This is the fruit of a Poppy (Papaver). Other fruits of this type are: Blue Poppy (Meconopsis), Prickly Poppy (Argemone). |
||||||||||||||||
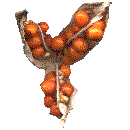 |
Loculicidal Capsule A Loculicidal Capsule is a dry dehiscent fruit, splitting along the locule (midrib of each ovary). This is the fruit of Stinking Gladwyn (Iris foetidissima). Other fruits of this type: Evening Primrose (Oenothera), Valotta (Cyrtanthus elatus), and members of the Violet and Lily Families. |
Circumscissile Capsule |
A Circumscissile Capsule is a dry dehiscent fruit, opening by splitting through the centre of the fruit, so that the top of the capsule lifts off like a lid. An example of this type of fruit is Pimpernel (Anagallis) A Septicidal Capsule splits along the septa (joints of the ovary) as in the Foxglove (Digitalis). DRY INDEHISCENT FRUITS  Achene |
An Achene is a single-seeded dry indehiscent fruit in which the seedcoat is not part of the fruit coat. This is the fruit of a Sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Other fruits of this type are: Buttercup (Ranunculus), Clematis (Clematis), Coreopsis (Coreopsis), Dahlia (Dahlia), English Marigold (Calendula), Zinnia (Zinnia). 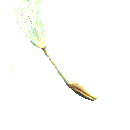 Cypsela A Cypsela is a single-seeded dry indehiscent fruit that develops from a one part inferior ovary (on the stalk side of the flower). They are sometimes included with Achenes. This is the fruit of a Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale). Other fruits of this type are found in the same plant family, the Daisy Family (Asteraceae).  Nut A Nut is a large single hardened achene. This is a Chestnut (Castanea sativa). Other fruits of this type are: Acorn (Quercus), Hazel (Corylus avellana), Hickory (Carya).  Nutlet This is not a classification that seems to be recognised everywhere, but the Mint Family (Lamiaceae) is a very large plant family, and has a particular type of seed which is not quite any of the normal ones, so I thought it should be included somewhere. The fruits of this family are single-seeded achene-like nutlets, which are held at the bottom of the calyx. This is the fruit of a Salvia (Salvia). All members of the Mint Family (Lamiaceae) have this type of fruit.  Caryopsis A Caryopsis is a simple dry indehiscent fruit, like an achene, but with the seedcoat fused with the fruit coat. This is the fruit of Sweetcorn (Zea). Other fruits of this type are all members of the Grass Family (Poaceae): Barley (Hordeum), Oats (Avena), Rice (Oryza), Rye (Secale), Wheat (Triticum).  Samara A Samara is an independent dry indehiscent fruit which has part of the fruit wall extended to form a wing (i.e. not a winged seed inside another type of seed pod). This is the fruit of a Maple (Acer). This is a Schizocarpic Samara, because the fruit splits into its separate Samaras. Other fruits of this type are: Ash (Fraxinus) - also Schizocarpic, Elm (Ulmus). | |||||||||||||